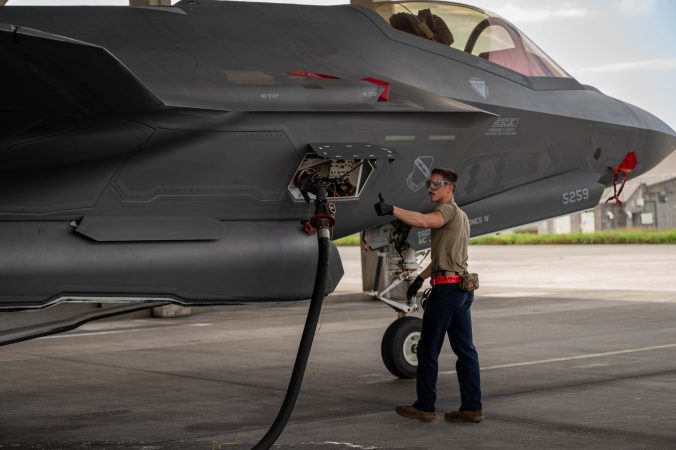
Airmen from the 20th Expeditionary Bomb Squadron perform post flight inspections on a B-52H Stratofortress at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England as part of Bomber Task Force Deployment 25-1, Nov. 5, 2024. BTF operations are U.S. Strategic Command’s means of conducting Dynamic Force Employment in support of the Department of Defense’s National Defense Strategy at the direction of the President of the United States. (U.S. Air Force Photo by Airman 1st Class Laiken King)

A B-52H Stratofortress from the 2nd Bomb Wing, Barksdale Air Force Base, La., releases a parachute after landing at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England as part of Bomber Task Force 25-1, Nov. 5, 2024. Strategic bomber task force missions enhance the readiness and training necessary to respond to any potential crisis or challenge across the globe. (U.S. Air Force Photo by Airman 1st Class Laiken King)

A U.S. Air Force B-52H Stratofortresses assigned to the 2nd Bomb Wing lands at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 8, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. The operational readiness of U.S. forces in all domains is vital to fostering strong partnerships, responding swiftly to crises, deterring threats and supporting our NATO Allies and partners. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

A U.S. Air Force B-52H Stratofortresses assigned to the 2nd Bomb Wing lands at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 8, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. A combat-ready force, with both extensive capabilities and wide-ranging capacity, is essential for effective deterrence and a swift, decisive response to any situation. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

A U.S. Air Force B-52H Stratofortresses assigned to the 2nd Bomb Wing lands at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 7, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. Bomber missions are a clear testament to the credibility and strength of our forces, as we navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain global security environment. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

A U.S. Air Force B-52H Stratofortresses assigned to the 2nd Bomb Wing lands at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 8, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. Strategic deterrence and decisive responses rely on a combat-ready force with both deep capabilities and broad capacity to address any challenge. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

Senior Airman Daniel Ramey, 20th Expeditionary Bomb Squadron crew chief, signals a B-52H Stratofortress to brake on the taxiway at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 7, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. By conducting strategic bomber missions, the U.S. enhances its readiness and training, remaining prepared to address any crisis or challenge on the global stage. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

A U.S. Air Force B-52H Stratofortresses assigned to the 2nd Bomb Wing lands at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 7, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. With a powerful and credible strategic bomber force, the U.S. strengthens the security and stability of our Allies and partners, ensuring readiness and deterrence in critical regions. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

A U.S. Air Force B-52H Stratofortresses assigned to the 2nd Bomb Wing lands at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 7, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. Bomber missions are a clear testament to the credibility and strength of our forces, as we navigate an increasingly complex and uncertain global security environment. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

A B-52H Stratofortress from the 2nd Bomb Wing, Barksdale Air Force Base, La., releases a parachute after landing at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England as part of Bomber Task Force 25-1, Nov. 5, 2024. Bomber task force missions are representative of the U.S. commitment to our Allies and partners and enhance regional security. (U.S. Air Force Photo by Airman 1st Class Laiken King)

A B-52H Stratofortress from the 2nd Bomb Wing, Barksdale Air Force Base, La., lands at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England as part of Bomber Task Force 25-1, Nov. 5, 2024. Bomber task force missions familiarize aircrew with air bases and operations in different Geographic Combatant Commands’ areas of operations.(U.S. Air Force Photo by Airman 1st Class Laiken King)

Senior Airman Daniel Ramey, 20th Expeditionary Bomb Squadron crew chief, signals a B-52H Stratofortress to brake on the taxiway at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 7, 2024, in preparation for Bomber Task Force 25-1. Our strategic bomber missions keep our forces ready and trained, ensuring we can respond swiftly to any global crisis or challenge that may arise. (U.S. Air Force photo by Senior Airman Mary Bowers)

U.S. Air Force Staff Sgt. Alejandro Castillo, a crew chief from the 20th Expeditionary Bomb Squadron, performs a post-flight inspection on a B-52H Stratofortress at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England as part of Bomber Task Force 25-1, Nov. 5, 2024. The U.S. maintains a strong, credible strategic bomber force that enhances the security and stability of Allies and partners. (U.S. Air Force Photo by Airman 1st Class Laiken King)

Airmen from the 20th Expeditionary Bomb Squadron perform post-flight inspections on a B-52H Stratofortress, at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England as part of Bomber Task Force Deployment 25-1, Nov. 5, 2024. U.S. forces are ready, postured, and well prepared to integrate with host-nation Allies and partners to deter threats and defend the Alliance. (U.S. Air Force Photo by Airman 1st Class Laiken King)

U.S. Air Force Airman 1st Class Sean Hathorn, internal security forces defender from the 423rd Security Forces Squadron, guards a B-52H Stratofortress at Royal Air Force Base Fairford, England, Nov. 5, 2024. “Deter and Defend” is ultimately designed to ensure the NATO Alliance remains strong, Allied citizens are safe, and shared values are secure. (U.S. Air Force Photo by Airman 1st Class Laiken King)