Editor’s Note: This story was updated at 11:25 a.m. on Feb. 24 to include information about the B-52 Bomber Task Force mission.
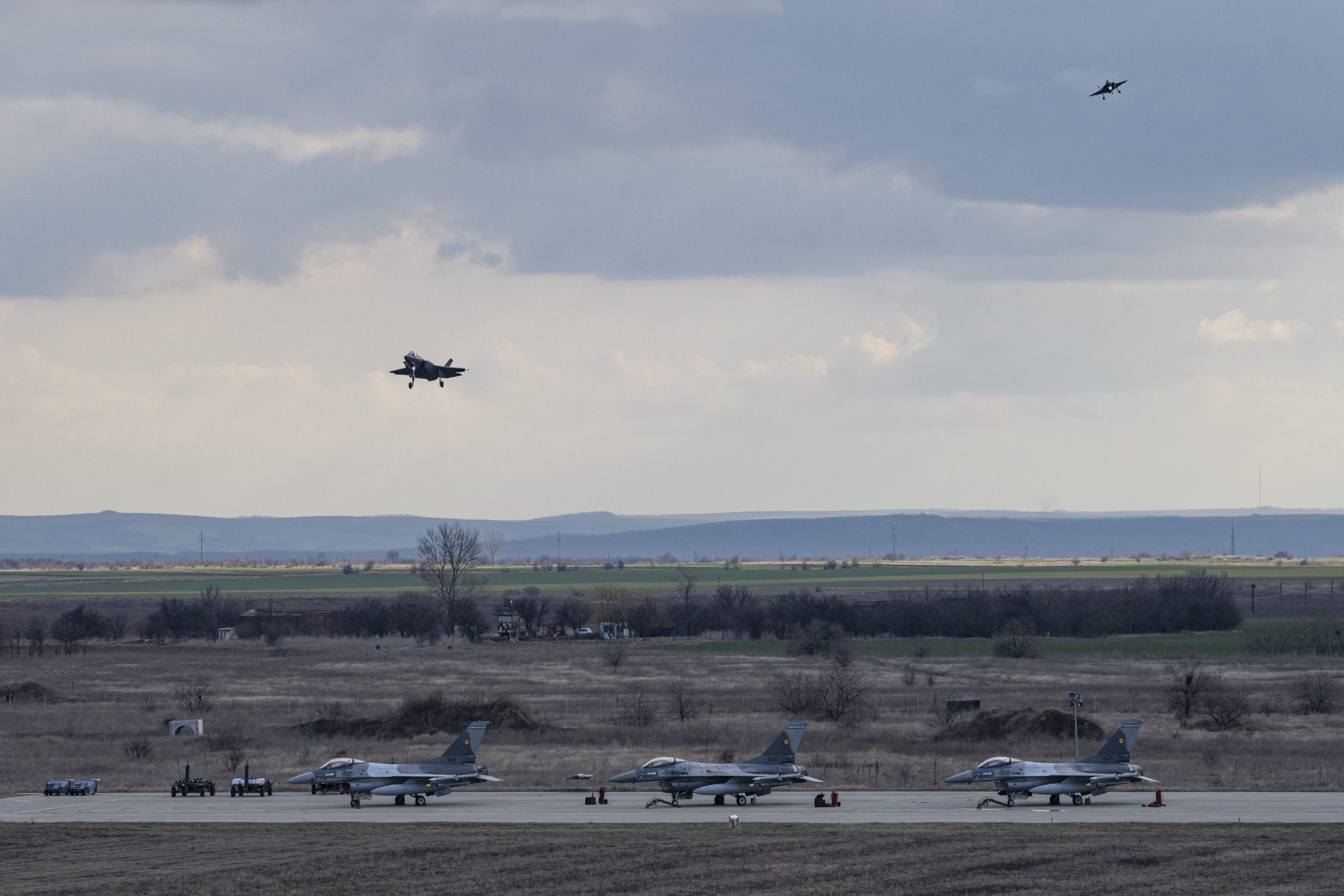
Six F-35s operating from Spangdahlem Air Base, Germany, ordered to NATO’s eastern front by President Joe Biden Feb. 22, arrived to the Baltic Sea and Black Sea regions Feb. 24 to reassure Allies as Russian forces move into Ukraine. At the same time, a B-52 from Minot Air Force Base, N.D., interacted with Polish fighters in the Black Sea region during a Bomber Task Force operation.
“We are facing a dynamic environment, and the deployment of F-35s to NATO’s eastern flank enhances our defensive posture and amplifies the Alliance’s interoperability,” said Gen. Jeffrey L. Harrigian, U.S. Air Force in Europe–Air Forces Africa commander, in a statement.
The F-35s, from the 34th Fighter Squadron at Hill Air Force Base, Utah, will join 24 F-15s and F-16s in Romania and Poland taking part in NATO enhanced air policing missions. USAFE said the aircraft will forward deploy “for a period of time” to the Baltics at Estonia’s Amari Air Base and Lithuania’s Siauliai Air Base, and to the Black Sea region at Romania’s Fetesti Air Base.
A Romanian defense official confirmed to Air Force Magazine that two of the F-35s arrived in Romania the morning of Feb. 24, joining eight F-16s at Fetesti. Romania shares a land border with Ukraine and has led an effort by the Bucharest nine, or B9, NATO eastern flank nations.
“Today [there] will be a B9 emergency meeting at [the] minister level and CHOD [chief of defense] level with U.S.,” the Romanian official said.
USAFE also confirmed that two B-52s from the 5th Bomb Wing deployed on a “long-planned Bomber Task Force Europe mission over the Arctic and Baltic Sea regions.” The bombers “joined forces with Sweden and Poland to enhance partner interoperability.” One B-52 “integrated with Polish MiG-29 aircraft amplifying support in the Baltic region,” according to a USAFE spokesman, while the second strategic bomber worked with Swedish Joint Terminal Attack Controllers to exercise Arctic operations.
France had offered to lead a NATO battle group in Romania, but the official said the alliance as a whole has yet to support the effort. In the meantime, the United States and other individual nations are contributing forces to the countries closest to the Russian threat to shore up the alliance.
Pentagon spokesman John F. Kirby said Feb. 23 that there were no plans to alter the command structure.
“Right now, they’re going to be under the command of Gen. [Tod D.] Wolters in his U.S. European Command hat,” he said in response to a question from Air Force Magazine.
Kirby could not say how long the strike fighters will be forward deployed.
“I want to remind you that they were already in Europe, they’re simply repositioning elsewhere in Europe,” he explained. “I don’t have a timeframe on how long that repositioning is going to be, except to say that it’ll be as long as we believe it’s necessary.”
Kirby said it also will depend on how long the host nations are willing to have them.
“This is really all about reassuring allies and partners and demonstrating that in tangible ways,” Kirby added.
The 8,500 U.S. troops on alert as part of a rapid NATO Response Force are “ready to go if called upon,” but still remained stateside, Kirby added.