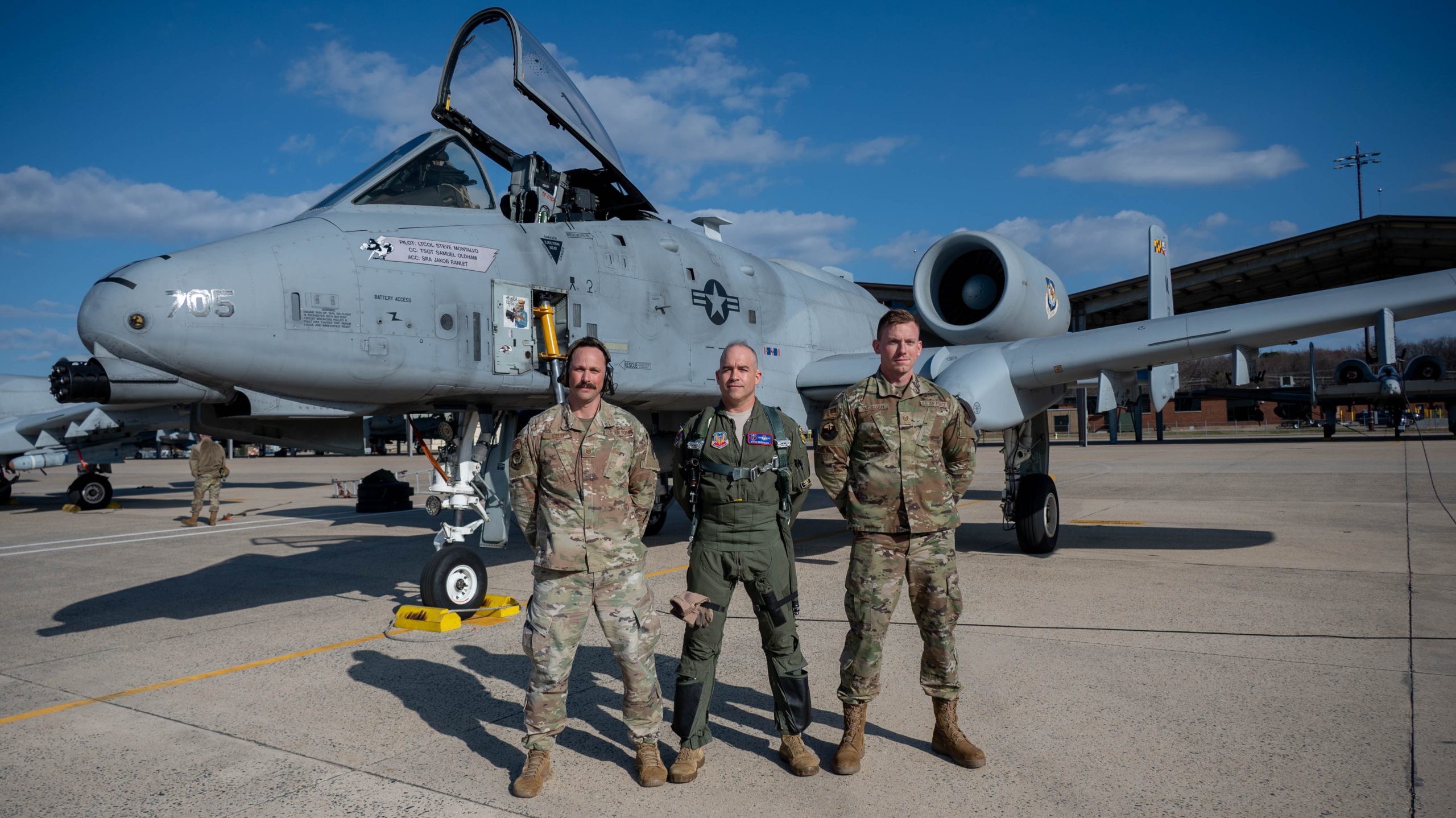
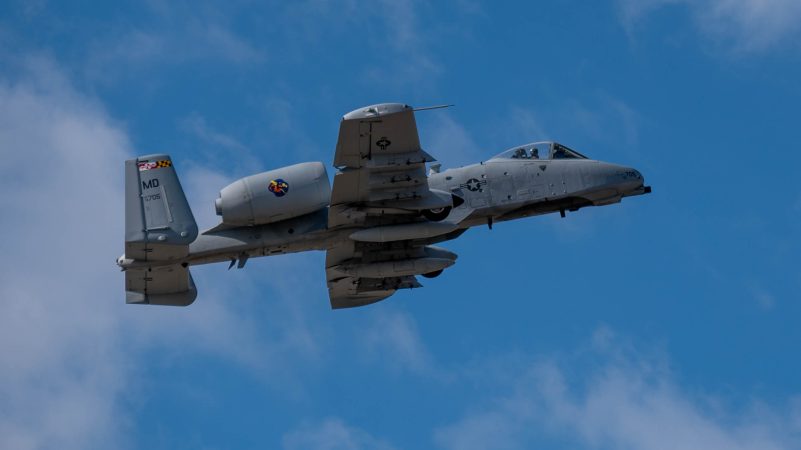
The first A-10 “Warthog” departed Warfield Air National Guard Base, Md., last week, the first step in a process that could leave Maryland Air Guard the only one among the 50 states without a flying mission. Negotiations to acquire a follow-on flying mission have stalled.
“Our Airmen—and the state of Maryland— should not be left as the only state without a flying mission,” said Brig. Gen. Drew E. Dougherty, state assistant adjutant general for Air in a release. “It’s more than tradition. It’s a critical component of our national security.”
An F-16 Air National Guard squadron will continue to operate out of Joint Base Andrews in Maryland, but that unit is actually assigned to the District of Columbia, and is not part of the Maryland Air Guard.
The first of the 21 A-10s from the ANG’s 175th Wing flew off to the boneyard at Davis-Monthan Air Force Base, Ariz., on March 26. When the last of the A-10s go, the wing will retain only the 175th Cyberspace Operations Group, pending an environmental analysis this fall. The final decision about the base’s future will be made by the next Secretary of the Air Force.

Former Secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall approved the transfer of the 121st Fighter Squadron and its Fighting Falcons from the D.C. Air National Guard to Maryland in a bid to preserve the flying mission for the state. The effort, supported by Gov. Wes Moore, Sen. Chris Van Hollen, and then-Sen. Ben Cardin, was apparently part of a poltitical deal in which the D.C. city government would secure rights to build a new stadium and return the NFL’s Washington Commanders to Washington, D.C., where they played before moving to suburban Maryland.
That decision was never finalized and further comment will be left to the Office of the Secretary of Defense, according to an Air Force spokesperson. Calls to OSD were referred to the White House’s National Security Council. The NSC did not immediately respond to inquiries.
Former President Joe Biden signed the RFK Stadium Revitalization Act, giving Washington, D.C., more control over the site of the former Robert F. Kennedy Stadium, which was recently razed. But Maryland’s apparent payback—the fighter squadron transfer, may not come to be. Asked about the transfer, Moore’s office said March 28 that the governor is “actively working with our Congressional Delegation and the new Administration in Washington to have a long-term flying mission for the Maryland Air National Guard.”
Van Hollen’s office could not immediately provide a comment.
A source familiar with the matter told Air & Space Forces Magazine that, as of now, there are no plans for the Maryland ANG regarding the squadron transfer.

Maryland Army National Guard Maj. Gen. Janeen L. Birckhead, adjutant general of Maryland, said the state is “fully committed to fighting for a future flying mission in Maryland.”
“Our Airmen deserve the opportunity to continue demonstrating their world-class skill in the air, as well as in cyberspace,” Birckhead added.
The Air Force is phasing out the beloved A-10 “tank-killer” jets, with plans to retire some 56 Warthogs in fiscal 2025. The service must find new missions for A-10 bases; some, like Moody Air Force Base, Ga., will get getting new F-35s. Others, like the Idaho Air National Guard’s 124th Fighter Wing and the Indiana ANG’s 122nd Fighter Wing are getting F-16s. Like Maryland’s 175th, the Ohio ANG’s 179th Airlift Wing is converting to a new mission; it transitioned to become the 179th Cyberspace Wing in 2023.
Maintaining a flying mission is important to elected officials, because aircraft are physical reflections of American power and because having them attracts federal and state investment, bringing jobs and emergency response capabilities to the area. A Purdue University study found that the 122nd Fighter Wing in Indiana contributes $113 million annually to the state’s economy, supporting 1,100 jobs.
The 104th Fighter Squadron has flown the A-10 for over four decades and its Airmen completed nine combat deployments in the past 20 years to Iraq and Afghanistan, striking Taliban and al-Qaida forces. It was the first unit to fly the A-10C variant into combat.
“The 175th Wing has proven time and again that we are capable of adapting, leading, and excelling in every mission we’re given,” Dougherty said.