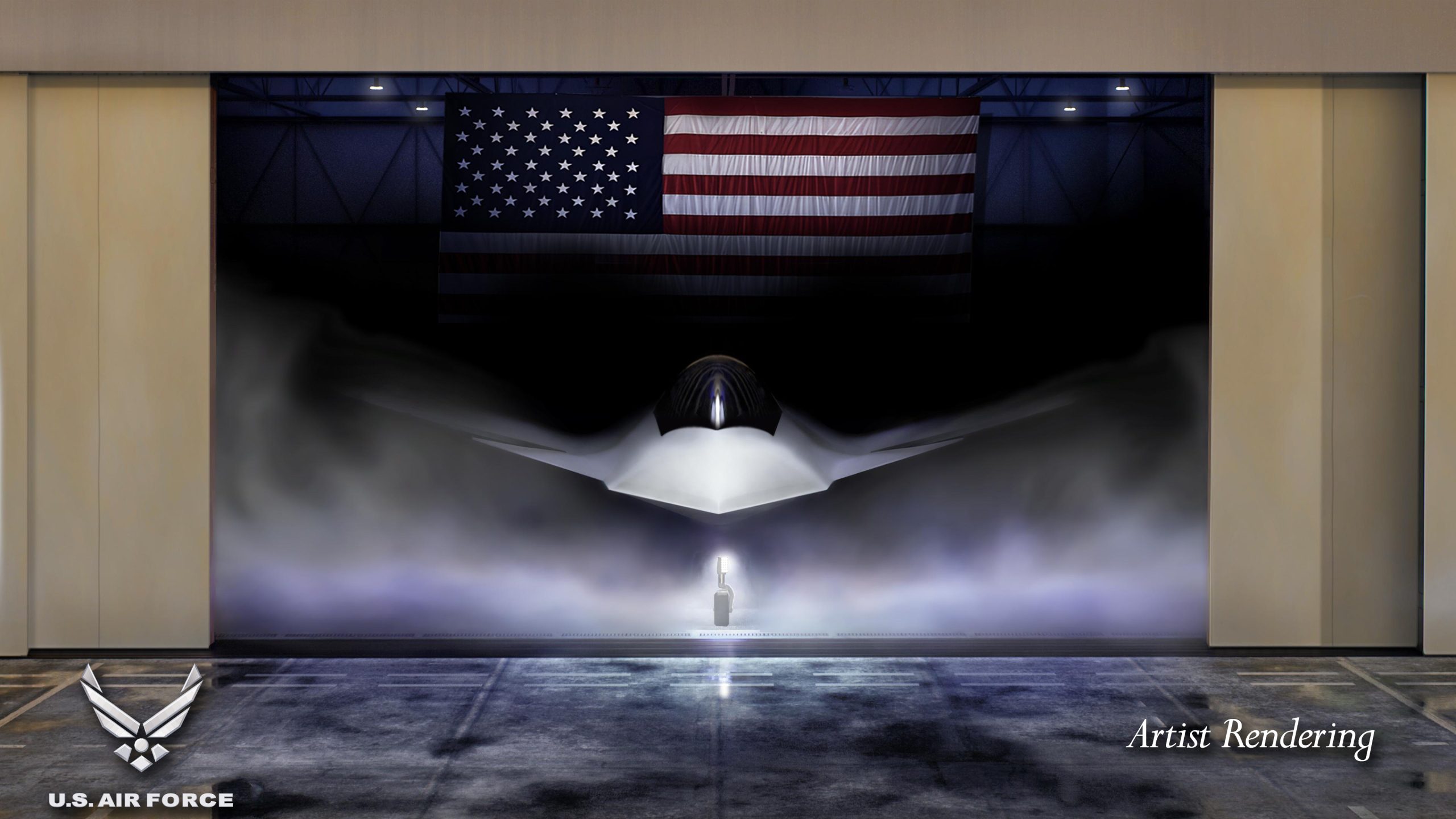
The Next-Generation Air Dominance fighter—announced as the F-47 by President Donald Trump this month—wasn’t going to be in the last Air Force budget request from President Joe Biden’s administration, former Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall revealed in a recent podcast, saying he believed there were higher priorities for the service to address.
Appearing on the Defense and Aerospace Report, Kendall said he paused the NGAD program last summer because “we just didn’t have enough money” in projected budgets to afford the planned sixth-generation fighter and other top priorities. While latter iterations of the budget included more funds, it was still not enough for all the most pressing needs, he said.
The Pentagon had previously projected that the NGAD program would cost nearly $20 billion over five years.
The Biden administration put together the fiscal 2026 budget to hand off to Trump’s team as it was preparing to leave office, and NGAD “wasn’t in it, and it was not a higher priority than the other things on my list,” Kendall said.
There was “no place left to trade off, within the Air Force budget, to fund it,” Kendall said of NGAD, which he acknowledged will cost “more than twice the price” of the F-35, which costs around $90 million per copy.
Kendall felt that certain missions—counter-space and air base defense being two he cited—were more important than NGAD. Without air base defense, he noted, “the F-22s, F-35s, and the F-47s will never get off the ground.”
How exactly the Trump administration will handle that delicate balance remains to be seen as it prepares its own 2026 budget submission.
“Again, it’s about affordability and it’s about strategic priorities, and the Air Force will have to sort it out,” Kendall said.
NGAD’s History
Trump, alongside Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, Air Force Chief of Staff Gen. David W. Allvin, and Lt. Gen. Dale R. White, announced Boeing would build the F-47, a major coup for the company after Lockheed Martin won the F-22 and F-35 competitions.
Former Air Force acquisition executive Andrew Hunter, who served under Kendall and also appeared on the podcast, said the NGAD submissions from Boeing and Lockheed Martin were “quite creative” and very close, technically.
Boeing may have had the edge, he suggested, because it saw the competition as a “must-win.”
“What you see sometimes on these things is, the incumbent is a little more risk-averse than the company that doesn’t have the installed [industrial] base at risk,” he said. The challenger can sometimes “be a little more innovative, or risk a little more in their proposal.”
The NGAD program, he added, was structured to encourage innovation. The F-47 will serve as “Increment 1 of NGAD, right? With the concept being that there will be future increments. And so it was designed not to be this ‘all or nothing,’ ‘hey, if you don’t win this, you’re out for the next three decades’ competition. It was designed to be something that…if you win, you have an order for 100, roughly, aircraft, but there’ll be other orders coming down the pike, and so you stay in the game.”
Hunter was quick to note, however, that “obviously time will tell how many increments ever get built.”
Kendall agreed that the offerings were very close technically, and that Lockheed “could have won this.”
Lockheed will have solid work with the F-35 for many years, he explained, but Boeing only had the F-15EX, which has a limited planned production, so Boeing, “if it was going to stay a viable fighter builder going forward, had to win this competition.”
Podcast host Vago Muradian asked how much past performance played a role in the competition, noting that Lockheed has two fifth-generation stealth fighter production programs under its belt, while Boeing has none, and Boeing has in recent years struggled to produce the KC-46 tanker, T-7 trainer and MQ-25 Navy tanker while losing nearly $10 billion on those programs.
But Kendall noted struggles with Lockheed over the price and schedule for F-35 Block 4 upgrades and sustainment, “so nobody’s got a clean record in terms of past performance.”
Hunter added that while past performance is nearly always a criteria, “it rarely is a differentiator.” He also said that technical performance is “rigorously validated” in such competitions.
“We don’t just take a company at their word if they say, ‘Yeah, our design meets your criteria for observability,’ right?” he said.
Kendall cautioned that “there’s risk with anybody we picked at this point. These are new designs. They’re aggressive designs. They’ve got a lot of new technologies [that] are going to be integrated together. That’s always very challenging. So I expect that there will be issues in risk that arise that have to be dealt with, no matter who won this.”
Calling the NGAD competition “viable,” Kendall suggested one of the companies “moved faster to demonstrate the key technologies, but the other one did get there and demonstrate them as well.” He didn’t say which entrant demonstrated capabilities more quickly.
“The designs are quite different,” he added. “ … It’s interesting how, when you give people the same problem, you can get engineers that come back with very different solutions. But I think we had a valid competition,” Kendall said.
The NGAD program has its roots in a program called the Aerospace Innovation Initiative started by Kendall when he was undersecretary of Defense for acquisition, technology, and logistics in the Obama administration. The initiative produced “X-planes” but not prototypes of the NGAD crewed airplane, called the Penetrating Combat Aircraft.
“When I started [it] … it was designed to mature technologies for a sixth-generation tactical aircraft,” he said. “There were certain desirable characteristics we were after, but I basically got $1 billion put into the five-year plan, into the budget, split evenly between the Navy, the Air Force and [the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency] to do a technology maturation program.”
When Kendall returned to the Pentagon as Secretary of the Air Force in 2020, “the X-planes had been built. They’ve been successful, and the Air Force had started down the path towards what is now known as the F-47,” he said.
The NGAD has always been intended as a “family of systems,” Kendall noted, with the crewed fighter only one element. Others include space-based sensors, offboard communications links, new weapons, and the Collaborative Combat Aircraft program.
The F-47 started out to be a “pretty direct descendant of the F-22…that’s essentially the design we have,” Kendall said, but under his tenure, it also took on the ability to “do other things, particularly controlling CCAs.”
Future
During the Oval Office announcement that Boeing had won the F-47 contract, Trump suggested a “toned down” version of the F-47 might be available for export, but Kendall thinks foreign sales are unlikely.
With the NGAD, “the emphasis was on getting as much capability as we could into the platform. That’s what has led to the very high price that the F-47 will have,” he said.
“I would be very surprised if any of our partners were prepared to pay that unit cost for a new aircraft. I’ve heard some stories that suggest that they would have bought the F-22 if we’d been willing to share the technology. I’m not sure that that’s true,” he said.
On top of that, he questioned whether allies would want the fighter if its capabilities were “toned down.” Some are pursuing sixth-gen fighters of their own.
The Navy will also not be buying the Air Force’s version of NGAD, though Hunter noted that the Navy’s own effort—called the F/A-XX—is sharing technology developed for the F-47.
“Even though we didn’t do a joint program here, like the F-35 … the approach means that at the architecture level, you’ve got compatibility with the Navy program,” Hunter said. The NGAD will be able to “seamlessly integrate” with the Navy’s systems, he said.
Northrop Grumman is competing for the F/A-XX against Boeing, with Lockheed having been eliminated. Kendall revealed that Northrop Grumman participated in the technology demonstrator program, but it was not chosen to go to the final round of the NGAD competition. Northrop has only revealed it “did not bid” the NGAD.
The Air Force has said that Boeing won the NGAD based on “best overall value” to the service.
Kendall said industrial base considerations—such as expanding the number of active-production fighter companies, so Lockheed would not have a monopoly—was not a consideration in the final analysis.
Lockheed has not yet said if it plans to protest the NGAD award to Boeing. If it does, the Government Accountability Office has 100 calendar days from the date of the protest to adjudicate whether the Air Force acted fairly in its choice of Boeing.
Other Priorities
In the never-released 2026 budget request where Kendall cut funding for NGAD, he said he instead prioritized missions like counter-space weapons and air base defense.
“We need to move forward aggressively with counter-space,” he said, noting that China now has scores of satellites designed to target U.S. forces and enable Chinese long-range fires. “So we had to respond to that, and I thought that was an important national priority … to defend our forces, but also our allies.”
Air base defense was another. China has “fielded literally thousands of weapons to attack” Air Force operating locations “with cruise missiles, ballistic missiles and hypersonics,” he said, and a cost-effective defense against them is crucial.
Air base defense is an Army mission, but that service’s limited number of Patriot and THAAD air defense systems “are not going to get you there,” especially given the Air Force’s Agile Combat Employment plan of operating from many locations and playing a shell game to protect them, Kendall said. Not long before the end of his tenure, Kendall pointed this out and said he’d be “comfortable” taking over the air base defense mission from the Army, since its plans won’t deliver the needed protection in a timely fashion.
“The economics just don’t work,” with Patriot and THAAD, he said, “So we need something more cost effective than those, and that was [also] not in the budget.”
F-35
Kendall said the Air Force “absolutely” needs Block 4 of the F-35.
“No question about it,” he said. “We’re in a race for technological superiority against a formidable opponent, and we cannot stand still. And 100-200 F-47s, that we’re not going to get for several years, is not going to keep us competitive. We’ve got to do more than that, and that has to include, I think, the Block 4 as well as the [Collaborative Combat Aircraft] and the Increment 2 of the CCA.”