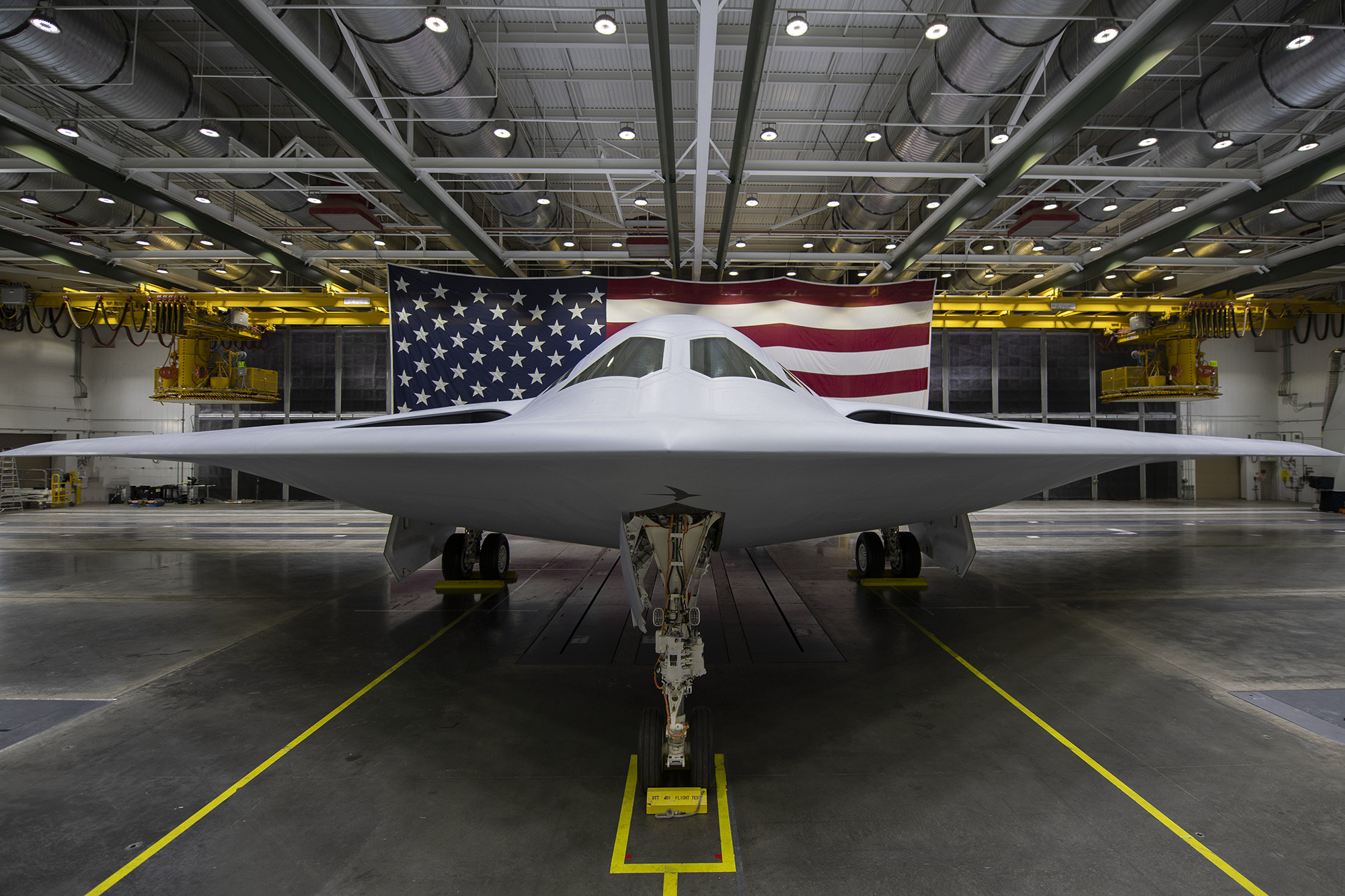
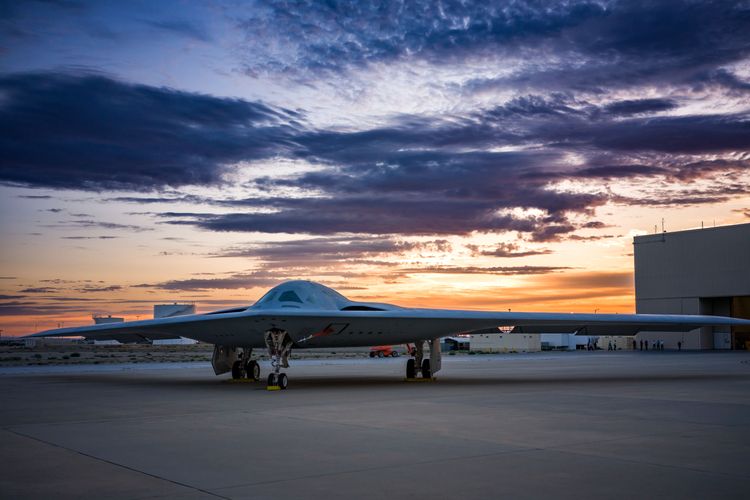
Northrop Grumman’s low-rate initial production contract for the B-21 bomber will only come after first flight, senior company officials confirmed on their third quarter earnings call, but they are confident the event will happen by the end of this year.
“First flight is a milestone that the Air Force is looking to achieve before they make that award,” Northrop chief executive officer Kathy Warden said Oct. 26.
“The first LRIP contracts will be awarded in the fourth quarter,” added Dave Keffer, Northrop’s executive vice president and chief financial officer. “That’s consistent with our expectations that we’ve described throughout the year, and reliant on first flight occurring between now and that contract award.
Keffer also said Northrop continues to “evaluate our performance and our outlook on the LRIP phase of the program each quarter. We did not make any significant changes to our estimates for that phase during the third quarter.”
The Air Force confirmed this week that the first B-21 has begun taxi tests at Northrop’s facilities at Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, Calif. Taxi tests are the last phase of preparation before first flight, but the Northrop executives did not hazard a guess about when that will take place. The B-21 rolled out of the Palmdale facility last December, an event driven by the fact that the secret aircraft would soon be conducting outdoor engine runs and taxi tests and could potentially be seen from nearby public land.
Warden also reiterated that Northrop won’t make any money on the B-21 in the LRIP phase, due to higher labor costs and inflation on the fixed-price contract.
“As we’ve consistently said, through the year, we are planning at a zero profitability,” she said. “But we have to perform and we are working hard to ensure” that the company hits its contractual marks. The B-21 will likely become profitable when it reaches full rate production, she has said in previous calls.
Keffer said he doesn’t expect that a continuing resolution will prevent an LRIP contract from being awarded, due to prior-year funding.
Asked whether the White House’s emergency supplemental request for $2.6 billion for classified Air Force programs affects the B-21, Warden said she could not comment.
“I will simply say we do continue to work with the Air Force on ensuring that we have the resources necessary to make the B-21 program successful,” she added. “We are progressing through ground testing and we’re on track to enter flight testing this year in line with the program baseline schedule.”
Munitions and Missiles
Warden said Northrop is seeing “growing demand” for its munitions, particularly the Advanced Anti-Radiation Guided Missile—Extended Range (AARGM-ER), which is the Air Force and Navy’s successor to the AGM-88 HARM anti-radiation missile.
“We’ve now received interest from more than a dozen countries, and just this week, the opportunity for a Foreign Military Sale to Finland was announced,” Warden said.
She also noted that in September, Northrop won a $705 million contract to develop the Stand-in Attack Weapon (SiAW) for the Air Force. The SiAW is “an air to ground weapon with the capability to strike mobile defense targets,” she said. “Our SiAW offering builds on the capabilities we provide with our high-speed AARGM missile, which is in production. Building off a mature product baseline, we’re able to reduce the developmental time, cost and risk to the SiAW program.”
She added that SiAW is “expected to be the air-to-ground weapon of choice for the F-35 and other fighters.”
Northrop felt comfortable bidding the fixed-price SiAW because both AARGM and SiAW “are building off of a mature technical baseline,” she said. Major primes are increasingly shying away from fixed-price contracts due to inflation and overruns that companies don’t want to absorb. L3Harris, for example, did not bid on SiAW, saying it was due to the fixed-price nature of the program.
“I have often said, fixed price is appropriate where it’s either a commercial item or an item that has reached a design maturity and been reduced to where we know what it will take to deliver that product,” Warden said.
“Because of the maturity of AARGM, and having a product line that met the Air Force requirements for SiAW … we are able to reduce cost [and] schedule, and of course, have better risk management. That allows us to have the risk tolerance to bid fixed price,” Warden added.
Warden previously has said Northrop will not pursue the Next-Generation Air Dominance program, suggesting that fixed-price elements played in that decision.
“In competition, there are many factors, but when a company has invested, and gotten the mature product line, there is a natural advantage that comes with that,” she said. “And that’s the situation we found ourselves in with SiAW.”